Global Laser Cladding Market
Published Date : December 29, 2025 Category: Electronics and Semiconductor
Advancing Surface Engineering Through High-Precision Material Deposition and Digital Manufacturing
Industry Landscape Snapshot
The Global Laser Cladding Market is gaining strong industrial relevance as manufacturers across heavy industries shift toward advanced surface engineering solutions that enhance component durability, performance efficiency, and lifecycle economics. As equipment operates under increasingly extreme thermal, mechanical, and corrosive environments, conventional coating and repair methods are proving insufficient to meet modern performance standards.
Laser cladding has emerged as a high-value manufacturing and repair technology, enabling precise deposition of metallic and composite materials onto substrate surfaces with minimal dilution and superior metallurgical bonding. The technology supports both surface enhancement and near-net-shape additive manufacturing, aligning closely with Industry 4.0 objectives and digital production workflows.
Driven by rising asset utilization, sustainability mandates, and the need to reduce unplanned downtime, laser cladding is transitioning from a niche repair technique into a strategic manufacturing capability across aerospace, energy, automotive, and industrial sectors.
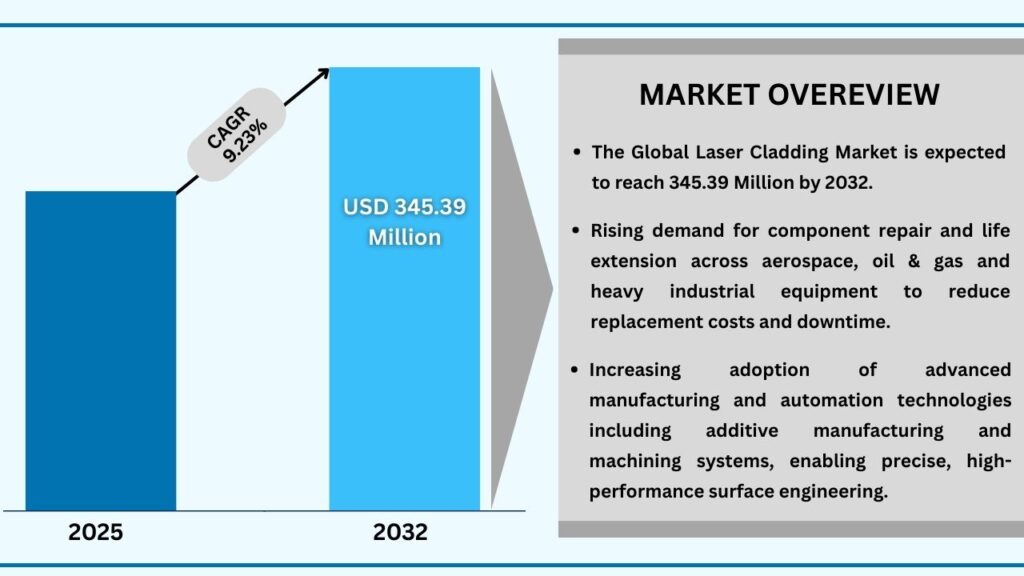
Global Laser Cladding Market – Overview
Global Laser Cladding Market – Market Definition & Scope
Functional Market Definition
The Laser Cladding Market comprises equipment systems, laser sources, materials, and integrated solutions used to deposit wear-resistant, corrosion-resistant, or functional layers onto metal components using high-energy laser beams.
Core market components include:
• High-power laser systems (diode, fiber, CO₂, YAG)- High-power laser sources form the technological backbone of laser cladding, delivering the energy required for precise melting and metallurgical bonding of materials. Diode and fiber lasers dominate due to high electrical efficiency, stable beam quality, and lower operating costs, while CO₂ and YAG lasers continue to serve niche applications requiring larger spot sizes or specific wavelength advantages.
• Powder- and wire-fed cladding technologies- Powder-fed and wire-fed systems define how material is delivered into the laser melt pool, directly influencing deposition efficiency and coating quality. Powder-fed cladding offers greater material flexibility and compositional control, whereas wire-fed cladding provides higher material utilization, lower waste, and improved process cleanliness.
• Metallic and composite cladding materials- Laser cladding materials include a wide range of metallic alloys and composite blends designed to enhance wear resistance, corrosion protection, and thermal stability. Common materials such as cobalt-, nickel-, iron-based alloys and carbide composites enable application-specific surface performance across demanding industrial environments.
• Automated and robotic laser cladding cells- Automated and robotic cladding systems integrate lasers with multi-axis motion platforms to enable consistent, repeatable processing of complex geometries. These systems improve productivity, reduce human error, and support large-scale industrial deployment in aerospace, automotive, and heavy machinery applications.
• Hybrid manufacturing and repair platforms- Hybrid platforms combine laser cladding with CNC machining, additive manufacturing, and digital control systems within a single production environment. This integration allows simultaneous material deposition and finishing, supporting near-net-shape manufacturing, rapid repair cycles, and flexible production workflows.
• Process control, monitoring, and digital integration systems
Laser cladding is applied across component repair, hardfacing, surface functionalization, and additive manufacturing, offering superior control over microstructure and coating thickness compared to thermal spray or welding methods.
Technology Evolution and Process Advancements
Manufacturing Innovation Trajectory
Continuous innovation in laser sources, material feed systems, and process automation is significantly expanding the commercial viability of laser cladding across high-volume and high-precision applications.
Key technological progress areas include:
• High-efficiency diode and fiber laser adoption
• Advanced powder delivery and wire-feed precision
• Multi-axis robotic integration for complex geometries
• Real-time process monitoring and closed-loop control
• Reduced heat-affected zones and lower material waste
• Integration with digital twins and smart factory systems
These developments are positioning laser cladding as both a cost-optimization tool and a performance-enhancement solution for next-generation manufacturing environments.
Regulatory Alignment and Industrial Standards
As laser cladding applications expand into safety-critical and regulated industries, compliance with quality, traceability, and reliability standards is becoming increasingly important. Aerospace certifications, energy-sector reliability norms, and automotive quality frameworks are shaping technology adoption.
Additionally, sustainability and resource-efficiency goals are indirectly accelerating laser cladding adoption, as the technology enables:
• Component life extension instead of replacement
• Reduced raw material consumption
• Lower energy usage compared to traditional repair methods
• Circular manufacturing and remanufacturing strategies
Role Within Modern Manufacturing Ecosystems
Laser cladding is increasingly embedded within advanced manufacturing and maintenance ecosystems, supporting:
• Predictive maintenance and component refurbishment
• Additive manufacturing of complex metal parts
• Hybrid machining and surface finishing workflows
• On-site and in-situ repair of high-value equipment
• Digital manufacturing and automation initiatives
Its versatility allows laser cladding to function across production, repair, and redesign cycles, strengthening its strategic value for asset-intensive industries.
Market Constraints and Adoption Challenges
Despite strong long-term prospects, the market faces several structural and technical limitations:
• High upfront capital expenditure for laser systems
• Skilled workforce requirements and process complexity
• Limited awareness among small and mid-scale manufacturers
• Competition from conventional thermal spray and welding technologies
• Material cost volatility for specialty alloys and powders
Addressing cost barriers and workforce skill gaps will be critical to accelerating broader market penetration.
Regional Market Dynamics
Asia-Pacific
Asia-Pacific represents the fastest-growing regional market, supported by large-scale industrial manufacturing, expanding automotive production, and strong investment in energy and infrastructure sectors. China, Japan, South Korea, and India are key contributors to regional growth.
North America
North America remains a technology-driven market, with strong demand from aerospace & defense, oil & gas, and advanced manufacturing sectors. High adoption of automation and additive manufacturing supports sustained growth.
Europe
Europe demonstrates steady expansion, driven by industrial machinery, automotive engineering, and renewable energy applications. Emphasis on sustainability, remanufacturing, and regulatory compliance strengthens laser cladding adoption in the region.
Competitive Structure and Industry Participation
The Global Laser Cladding Market features a mix of:
• Laser system manufacturers
• Industrial automation providers
• Material and powder suppliers
• Integrated solution providers
• Specialized service companies
Recent Industry Developments
Expansion of Automated Cladding Systems
Manufacturers are investing in fully automated, robotic laser cladding cells to support high-throughput industrial applications.
Cross-Sector Technology Collaboration
Collaborations between laser technology providers, material suppliers, and end-use industries are accelerating application-specific customization and deployment.
Competitive differentiation is shaped by process reliability, system integration capability, material expertise, and after-sales support. Strategic partnerships between laser OEMs, robotic integrators, and end-users are increasingly defining market leadership.
Strategic Outlook and Market Trajectory
Future growth of the Laser Cladding Market will be driven by:
• Rising demand for wear- and corrosion-resistant surfaces
• Growth of additive and hybrid manufacturing models
• Increased focus on asset life extension and sustainability
• Digitalization of manufacturing and maintenance operations
• Expansion of energy, aerospace, and heavy industrial sectors
Laser cladding is expected to evolve from a specialized surface treatment technology into a core pillar of advanced manufacturing and industrial repair strategies.
Conclusion
The Global Laser Cladding Market is entering a phase of sustained expansion as industries seek precision-driven, resource-efficient, and high-performance manufacturing solutions. Supported by technological innovation, automation, and growing application diversity, laser cladding is becoming an essential enabler of modern industrial production and asset management. As manufacturing ecosystems continue to evolve, laser cladding will play an increasingly central role in shaping the future of surface engineering and additive manufacturing.
At Advantia Business Consulting, we support manufacturers, technology providers, and industrial stakeholders in translating laser cladding innovations into scalable, high-value manufacturing strategies. Our expertise spans market intelligence, technology assessment, commercialization planning, and competitive benchmarking—helping organizations optimize surface engineering investments, enhance production efficiency, and strengthen long-term competitiveness. Partner with Advantia Business Consulting to unlock strategic insights and drive sustainable growth in the evolving laser cladding ecosystem.